Micromanufacturing: Revolutionizing Small-Scale Production
The fusion of advanced technology and miniaturization is reshaping industrial landscapes. Micromanufacturing, a cutting-edge approach to small-scale production, is gaining traction across various sectors. This innovative methodology leverages precision engineering and sophisticated materials to create microscopic components and devices, opening new frontiers in manufacturing capabilities and product design.
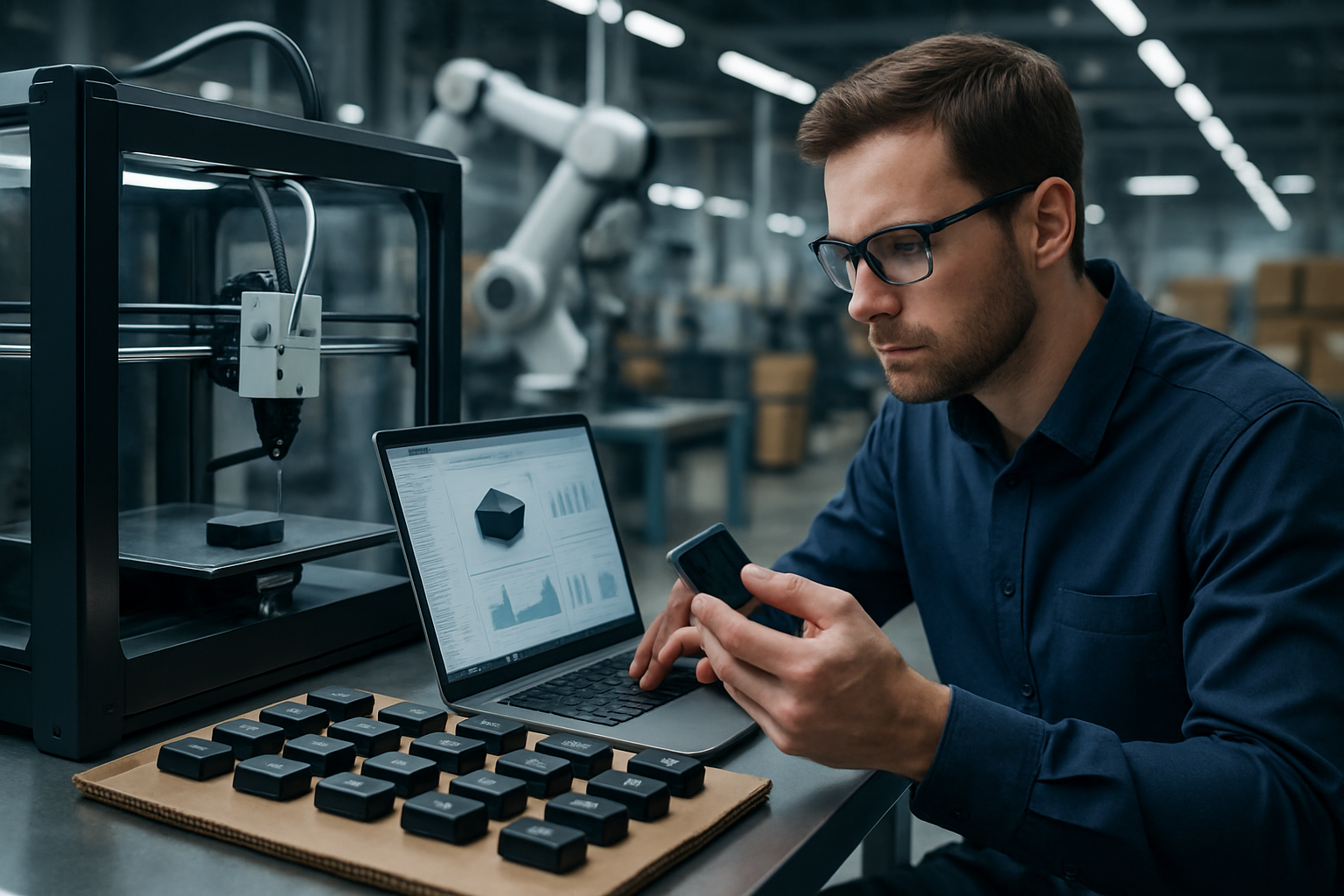

The Evolution of Small-Scale Production
Micromanufacturing represents a significant leap forward in the realm of small-scale production. Traditionally, manufacturing processes were limited by the capabilities of large-scale machinery and the constraints of manual labor. The advent of micromanufacturing has shattered these limitations, allowing for the creation of components at a microscopic level with astonishing precision.
This evolution began with the development of micromachining techniques in the late 20th century. As technology advanced, new methods such as photolithography and laser micromachining emerged, enabling the production of increasingly smaller and more complex parts. The integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems further accelerated the progress, allowing for unprecedented control over the manufacturing process.
Key Technologies Driving Micromanufacturing
Several cutting-edge technologies are at the heart of micromanufacturing’s success. Micro-electrical discharge machining (Micro-EDM) uses electrical discharges to remove material with extreme precision, creating intricate shapes and patterns. Laser micromachining employs focused laser beams to ablate material, offering unparalleled accuracy in cutting and shaping microscopic components.
Additive manufacturing techniques, such as two-photon polymerization, have revolutionized the production of three-dimensional microstructures. This process allows for the creation of complex geometries at the nanoscale, opening up new possibilities in fields like biomedical engineering and optical device fabrication.
Additionally, advanced materials play a crucial role in micromanufacturing. The development of specialized alloys, ceramics, and polymers has enabled the production of components with enhanced properties, such as improved strength-to-weight ratios and biocompatibility.
Applications Across Industries
The impact of micromanufacturing spans a wide range of industries, each benefiting from its unique capabilities. In the medical field, micromanufactured components are revolutionizing the design of implantable devices, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools. Miniaturized sensors and actuators produced through these techniques are enhancing the functionality and reducing the size of medical instruments, leading to less invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes.
The electronics industry has embraced micromanufacturing to create ever-smaller and more powerful devices. From microprocessors to MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) devices, this technology enables the production of components that drive innovation in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and computing.
Aerospace and defense sectors utilize micromanufacturing to produce lightweight, high-performance parts for aircraft and satellites. The ability to create complex geometries at microscopic scales allows for the optimization of component designs, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and enhanced performance.
Economic Implications and Market Trends
The rise of micromanufacturing is reshaping market dynamics and creating new economic opportunities. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are finding themselves on more equal footing with larger corporations, as the technology reduces the barriers to entry for producing high-precision components.
The global market for micromanufacturing equipment and services is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% in the coming years. This growth is driven by increasing demand for miniaturized components across various industries and the continuous advancement of micromanufacturing technologies.
Moreover, the localization of production is becoming more feasible with micromanufacturing. The reduced footprint of equipment and the ability to produce small batches economically are enabling companies to bring manufacturing closer to their end-users, potentially disrupting traditional supply chain models.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its promising potential, micromanufacturing faces several challenges. The high initial investment required for equipment and the need for specialized expertise can be barriers for some businesses. Quality control at such small scales presents unique difficulties, requiring advanced inspection and testing methods.
Looking ahead, the future of micromanufacturing appears bright. Ongoing research in areas such as nanotechnology and advanced materials is expected to further expand the capabilities of micromanufacturing. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into the manufacturing process promises to enhance precision and efficiency, potentially leading to fully autonomous micromanufacturing systems.
As industries continue to demand smaller, more complex components, micromanufacturing is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of production. Its ability to bridge the gap between nano and macro scales opens up new possibilities for innovation across multiple sectors, promising to drive technological advancements and economic growth in the years to come.
Maximizing Micromanufacturing Potential
-
Invest in employee training to develop expertise in micromanufacturing technologies
-
Collaborate with research institutions to stay at the forefront of technological advancements
-
Consider partnerships with complementary businesses to share resources and knowledge
-
Implement rigorous quality control measures tailored to microscale production
-
Explore opportunities for customization and small-batch production to meet niche market demands
In conclusion, micromanufacturing stands as a testament to human ingenuity and technological progress. As this field continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new realms of possibility in product design and manufacturing efficiency. Businesses that embrace and master micromanufacturing techniques will be well-positioned to lead in an era where the smallest components often make the biggest impact.