Redefining Spectrum Efficiency: Dynamic Spectrum Access in Telecommunications
The world of telecommunications is on the brink of a paradigm shift. As demand for wireless connectivity skyrockets, traditional methods of spectrum allocation are proving insufficient. Enter Dynamic Spectrum Access (DSA), a revolutionary approach that promises to transform how we utilize our limited radio frequency resources. But what exactly is DSA, and how could it reshape the future of connectivity?
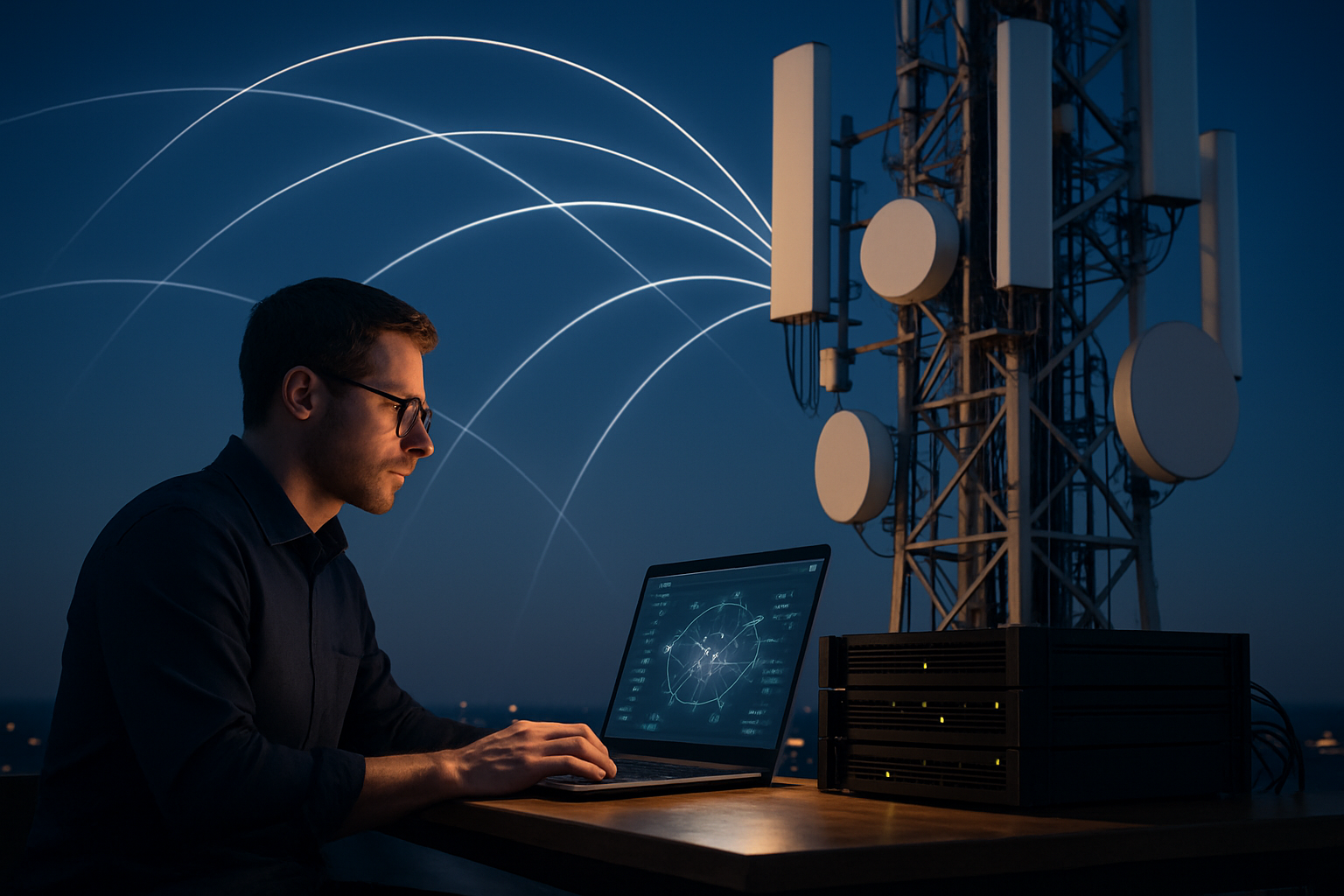

The spectrum crunch is not just a theoretical concern. It’s already impacting users in densely populated urban areas, where network congestion during peak hours can lead to dropped calls, slow data speeds, and frustrating connectivity issues. As we move towards an increasingly connected world, this problem is only set to worsen unless innovative solutions are implemented.
Understanding Dynamic Spectrum Access
Dynamic Spectrum Access represents a radical departure from conventional spectrum management techniques. At its core, DSA is an intelligent, adaptive approach to spectrum utilization that allows for real-time, opportunistic access to available frequency bands.
Unlike static allocation, DSA employs advanced sensing and cognitive radio technologies to identify and use unoccupied portions of the spectrum. This dynamic approach enables multiple users or services to share the same frequency bands without causing harmful interference to each other.
The key components of DSA include:
-
Spectrum sensing: Devices equipped with DSA capabilities continuously monitor the radio environment to detect unused spectrum.
-
Spectrum decision: Based on the sensing results, the system determines which frequencies are available for use.
-
Spectrum sharing: Multiple users can access the same spectrum simultaneously through careful coordination and interference management.
-
Spectrum mobility: Users can seamlessly switch between different frequency bands as availability changes.
The Technological Foundations of DSA
The implementation of Dynamic Spectrum Access relies on several cutting-edge technologies and concepts:
-
Cognitive Radio: This is the cornerstone of DSA. Cognitive radios are intelligent devices capable of adapting their transmission parameters based on the surrounding radio environment.
-
Software-Defined Radio (SDR): SDR technology allows for flexible, programmable radio systems that can operate across a wide range of frequencies and modulation schemes.
-
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: These technologies enable DSA systems to learn from past experiences, predict spectrum usage patterns, and make intelligent decisions about spectrum allocation.
-
Geolocation Databases: These databases provide information about spectrum availability in specific geographic areas, helping DSA systems make informed decisions about frequency usage.
-
Spectrum Sensing Algorithms: Advanced algorithms are employed to detect and classify signals, identify spectrum holes, and ensure non-interference with primary users.
Potential Applications and Benefits
The implementation of Dynamic Spectrum Access could bring about numerous benefits across various sectors:
-
Improved Spectrum Efficiency: By allowing opportunistic access to underutilized spectrum, DSA can significantly increase overall spectrum efficiency.
-
Enhanced Connectivity: In urban areas, DSA could help alleviate network congestion by dynamically allocating spectrum where it’s needed most.
-
Rural Broadband Access: DSA could make it economically viable to provide broadband services in remote areas by utilizing available TV white spaces.
-
Public Safety Communications: Emergency responders could benefit from more reliable and flexible communications systems that can adapt to changing conditions.
-
Smart Cities: DSA could support the massive number of connected devices expected in future smart city implementations.
-
Cognitive Sensor Networks: Environmental monitoring and industrial IoT applications could leverage DSA for more efficient and reliable data transmission.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
While the potential of Dynamic Spectrum Access is immense, its widespread adoption faces several challenges:
-
Technical Complexity: Implementing DSA requires sophisticated hardware and software, which can be costly and complex to deploy at scale.
-
Interference Management: Ensuring that DSA systems do not cause harmful interference to primary spectrum users is crucial and requires robust algorithms and protocols.
-
Standardization: The development of industry-wide standards for DSA technologies is necessary for interoperability and widespread adoption.
-
Regulatory Framework: Current spectrum regulations in many countries are not designed to accommodate dynamic access. Significant policy changes will be required to fully realize the benefits of DSA.
-
Security Concerns: As with any wireless technology, ensuring the security and privacy of DSA systems is paramount to prevent malicious interference or unauthorized spectrum access.
The Road Ahead: Towards a Dynamic Spectrum Future
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in telecommunications, Dynamic Spectrum Access represents a promising solution to our growing connectivity challenges. By fundamentally changing how we approach spectrum management, DSA has the potential to unlock new levels of efficiency and innovation in wireless communications.
However, realizing this potential will require concerted effort from industry stakeholders, regulators, and researchers. As trials and pilot projects continue to demonstrate the viability of DSA, we can expect to see increased investment and development in this transformative technology.
The future of telecommunications is dynamic, adaptive, and intelligent. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in wireless connectivity, Dynamic Spectrum Access may well be the key to unlocking a truly connected world.